Database administrators need simple and quick ways to manage their SQL Server environment. SQL Admin Toolset provides 24 essential desktop tools for SQL Server to save time by simplifying routine administrative and troubleshooting tasks.
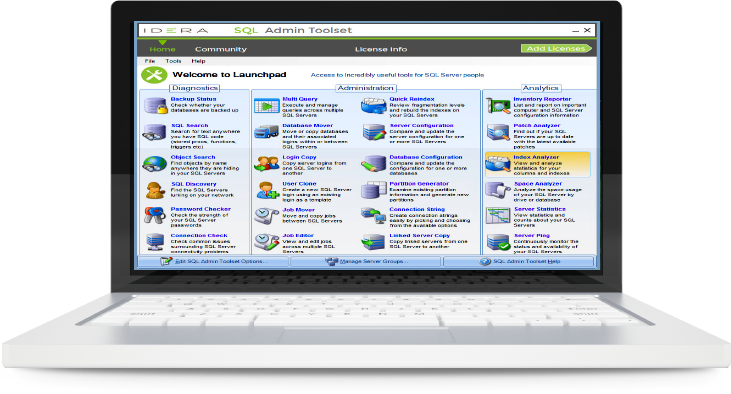
SQL Admin Toolset helps you manage, discover, and explore your SQL Server environment. Avoid spending countless hours on routine administration, diagnostics, and analytics tasks across multiple instances. Skip writing and maintaining complex and error-prone scripts.

SBetter manage logins and security.
Copy logins between instances to keep logins synchronized between instances. Evaluate and strengthen password policies to see which logins are at risk to increase the strength of passwords. Test instance connections and troubleshoot common issues surrounding connectivity problems to ensure that users can connect to instances.
Better manage objects.
Find specific words or text phrases in SQL schema objects. View columns and indexes contained in specific tables and view their properties and performance statistics within instances. Find tables and objects by searching for specific words or text phrases in object names.


Better manage migrations.
Create new logins by using existing logins as templates by cloning immediately or generating T-SQL scripts for preview and editing. Move and copy databases within or across instances while preserving their data files and logins to (for example) transfer performance intensive databases to faster storage to speed up performance.
Better manage inventory and configurations.
Identify disk space usage across instances by drive or database to proactively plan capacity for instances, databases, and hardware. Collect real-time statistics and performance counters to determine the health of instances. Keep instances updated with supported versions, and latest patches and hotfixes.

- Backup Status
Safeguard that SQL Server databases have proper backups, identify databases that have no backup, know when databases were last backed up, identify disabled and failing backup plans, and view backup status across all instances. When it is time to restore, do not find out that recent backups do not exist. - SQL Search
Find words and phrases in SQL code, perform a global search and replace, search for exact words, phrases, and wildcards, see the full SQL source in search results, and save search results. Save time on tasks like updating copyright notices and changing all usages of stored procedure calls. - Object Search
Find objects across SQL Server environments, search for words and phrases used in object names, search across all objects in instances and server groups, search using wildcards, and save search results. Determine where particular objects exist and the number of specific objects residing in instances. - SQL Discovery
Find new and rogue SQL Server instances on networks, use multiple scan types to increase search effectiveness, and check the configuration of discovered instances. Identify and group newly found instances. Then properly lock down these instances to prevent future security issues. - Password Checker
Find weak passwords that make SQL Server instances vulnerable to attack, replace weak passwords with strong passwords, use industry best practices, and company password policies to test password strength, and save test results. Eliminate weak passwords and security holes from instances. - Connection Check
Identify connection problems for SQL Server instances, and diagnose why users cannot login to instances. Check the status of instances, host computers, network connections and client machines. Resolve connection problems using best practices.
- Multi Query
Run queries against multiple SQL Server instances and databases at the same time, make changes in bulk, create and reuse target lists of instances and databases, save the returned result sets, and track statistics and object properties over time. Quickly perform operations on multiple instances at once. - Database Mover
Move and copy databases from one SQL Server instance to another, move and copy logins along with the database, copy and rename a database on the same instance, and relocate the data files for a database to a different storage device while keeping the database on the same instance. - Login Copy
Synchronize SQL Server instances logins between two instances, compare instances to see which logins do not match, and supplement existing backup and recovery scripts by capturing the logins stored outside the databases at the server level. Easily administer logins on parallel environments. - User Clone
Create new SQL Server logins using existing logins as templates, create new users by cloning existing users, and immediately perform the clone operation. Generate, preview and edit T-SQL scripts. Copy logins across instances to maintain consistent permissions on every instance. - Job Mover
Move SQL Server jobs from one instance and database to another, copy jobs from one instance and database to another, preserve assigned user privileges when moving jobs, and copy jobs from staging to production servers. - Job Editor
Edit SQL Server jobs, perform updates to jobs in bulk across an environment, get a comprehensive view of all jobs in SQL Server environments, see full job properties like status, owner and last run outcome, and export data to use in scripts and applications.
- Quick Reindex
Reindex SQL Server instances, view fragmentation levels across indexes, rebuild and reorganize indexes to reduce fragmentation levels, filter results by instance, database and table, sort indexes based on fragmentation level, size and name, and filter to hide small and disabled indexes. - Server Configuration
Review, compare, and edit configuration settings of one and multiple SQL Server instances, diagnose problems and identify unwanted differences, identify configuration changes over time, roll out configuration changes to one and multiple instances, and report on configuration settings. - Database Configuration
Review, compare and edit configuration settings of one and multiple databases, diagnose problems and identify unwanted differences, identify configuration changes over time, roll out configuration changes to one and multiple databases, and report on configuration settings by instance and by server group. - Partition Generator
Create and manage SQL Server table partitions, determine whether tables are partitioned and should be partitioned, create partitions and specify data ranges, and change existing partitions by merging and splitting data ranges. - Connection String
Build SQL Server connection strings, eliminate the need to research and memorize all available connection string options, and test connection strings before copying them into SQL code. - Linked Server Copy
Easily copy login credentials for remotely linked SQL Server servers, view all available linked servers, monitor the status of login passwords that are movable, easily see the move status of copied permissions that, and maintain remote connectivity for query login permission.
- Inventory Reporter
Capture inventory and configuration details about SQL Server instances and their host computers, compare captured inventory data against previous snapshots and other instances, highlight differences, create inventory reports, and export data for use in scripts and application. - Patch Analyzer
Keep SQL Server instances properly patched, identify unsupported versions of instances running on servers, identify available service packs and hotfixes, and view Microsoft Knowledge Base articles associated with service packs and hotfixes. - Index Analyzer
Optimize the use of indexes on SQL Server databases, view index usage, analyze the usefulness of each index, examine selectivity levels across indexes, and see vital statistics essential for balancing the index usage for data updates and queries. Apply correct indexes and eliminating bad ones. - Space Analyzer
Identify the disk space and storage usage for SQL Server instances, identify runaway log files, proactively anticipate when new instances need to be brought online, and plan for new databases and hardware upgrades. - Server Statistics
Determine the health of SQL Server instances by collecting real-time statistics, view detailed metrics (such as backup devices, databases, error logs, locks, logins, performance counters, processes, and SQL agent jobs), and compare statistics from one instance to another. - Server Ping
Monitor the status of SQL Server instances across the environment by routinely pinging specified instances. Execute the tool as centralized user interface and as a system tray service that alerts when instances go offline and become unhealthy.
- Install on cloud virtual machines
Unify your control by running SQL Admin Toolset on cloud virtual machines with Windows — such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Azure virtual machines. - Manage SQL Server on cloud virtual machines
Manage your SQL Server instances running on cloud virtual machines — such as Amazon EC2 and Azure virtual machines. - Monitor hybrid environments with a single tool
Save time by using the same administration tool for SQL Server databases on-premises (on your physical and virtual machines); and in the private, public, and government cloud (on virtual machines). - Access mapped cloud drives
Get the most out of the cloud with cloud storage that is mapped as network drives or removable drives on Windows with SQL Admin Toolset. For example, map storage to Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and Azure Blob Storage.
- Diagnostics
-
- Backup Status
Safeguard that SQL Server databases have proper backups, identify databases that have no backup, know when databases were last backed up, identify disabled and failing backup plans, and view backup status across all instances. When it is time to restore, do not find out that recent backups do not exist. - SQL Search
Find words and phrases in SQL code, perform a global search and replace, search for exact words, phrases, and wildcards, see the full SQL source in search results, and save search results. Save time on tasks like updating copyright notices and changing all usages of stored procedure calls. - Object Search
Find objects across SQL Server environments, search for words and phrases used in object names, search across all objects in instances and server groups, search using wildcards, and save search results. Determine where particular objects exist and the number of specific objects residing in instances. - SQL Discovery
Find new and rogue SQL Server instances on networks, use multiple scan types to increase search effectiveness, and check the configuration of discovered instances. Identify and group newly found instances. Then properly lock down these instances to prevent future security issues. - Password Checker
Find weak passwords that make SQL Server instances vulnerable to attack, replace weak passwords with strong passwords, use industry best practices, and company password policies to test password strength, and save test results. Eliminate weak passwords and security holes from instances. - Connection Check
Identify connection problems for SQL Server instances, and diagnose why users cannot login to instances. Check the status of instances, host computers, network connections and client machines. Resolve connection problems using best practices.
- Backup Status
- Administration I
-
- Multi Query
Run queries against multiple SQL Server instances and databases at the same time, make changes in bulk, create and reuse target lists of instances and databases, save the returned result sets, and track statistics and object properties over time. Quickly perform operations on multiple instances at once. - Database Mover
Move and copy databases from one SQL Server instance to another, move and copy logins along with the database, copy and rename a database on the same instance, and relocate the data files for a database to a different storage device while keeping the database on the same instance. - Login Copy
Synchronize SQL Server instances logins between two instances, compare instances to see which logins do not match, and supplement existing backup and recovery scripts by capturing the logins stored outside the databases at the server level. Easily administer logins on parallel environments. - User Clone
Create new SQL Server logins using existing logins as templates, create new users by cloning existing users, and immediately perform the clone operation. Generate, preview and edit T-SQL scripts. Copy logins across instances to maintain consistent permissions on every instance. - Job Mover
Move SQL Server jobs from one instance and database to another, copy jobs from one instance and database to another, preserve assigned user privileges when moving jobs, and copy jobs from staging to production servers. - Job Editor
Edit SQL Server jobs, perform updates to jobs in bulk across an environment, get a comprehensive view of all jobs in SQL Server environments, see full job properties like status, owner and last run outcome, and export data to use in scripts and applications.
- Multi Query
- Administration II
-
- Quick Reindex
Reindex SQL Server instances, view fragmentation levels across indexes, rebuild and reorganize indexes to reduce fragmentation levels, filter results by instance, database and table, sort indexes based on fragmentation level, size and name, and filter to hide small and disabled indexes. - Server Configuration
Review, compare, and edit configuration settings of one and multiple SQL Server instances, diagnose problems and identify unwanted differences, identify configuration changes over time, roll out configuration changes to one and multiple instances, and report on configuration settings. - Database Configuration
Review, compare and edit configuration settings of one and multiple databases, diagnose problems and identify unwanted differences, identify configuration changes over time, roll out configuration changes to one and multiple databases, and report on configuration settings by instance and by server group. - Partition Generator
Create and manage SQL Server table partitions, determine whether tables are partitioned and should be partitioned, create partitions and specify data ranges, and change existing partitions by merging and splitting data ranges. - Connection String
Build SQL Server connection strings, eliminate the need to research and memorize all available connection string options, and test connection strings before copying them into SQL code. - Linked Server Copy
Easily copy login credentials for remotely linked SQL Server servers, view all available linked servers, monitor the status of login passwords that are movable, easily see the move status of copied permissions that, and maintain remote connectivity for query login permission.
- Quick Reindex
- Analytics
-
- Inventory Reporter
Capture inventory and configuration details about SQL Server instances and their host computers, compare captured inventory data against previous snapshots and other instances, highlight differences, create inventory reports, and export data for use in scripts and application. - Patch Analyzer
Keep SQL Server instances properly patched, identify unsupported versions of instances running on servers, identify available service packs and hotfixes, and view Microsoft Knowledge Base articles associated with service packs and hotfixes. - Index Analyzer
Optimize the use of indexes on SQL Server databases, view index usage, analyze the usefulness of each index, examine selectivity levels across indexes, and see vital statistics essential for balancing the index usage for data updates and queries. Apply correct indexes and eliminating bad ones. - Space Analyzer
Identify the disk space and storage usage for SQL Server instances, identify runaway log files, proactively anticipate when new instances need to be brought online, and plan for new databases and hardware upgrades. - Server Statistics
Determine the health of SQL Server instances by collecting real-time statistics, view detailed metrics (such as backup devices, databases, error logs, locks, logins, performance counters, processes, and SQL agent jobs), and compare statistics from one instance to another. - Server Ping
Monitor the status of SQL Server instances across the environment by routinely pinging specified instances. Execute the tool as centralized user interface and as a system tray service that alerts when instances go offline and become unhealthy.
- Inventory Reporter
- Cloud
-
- Install on cloud virtual machines
Unify your control by running SQL Admin Toolset on cloud virtual machines with Windows — such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Azure virtual machines. - Manage SQL Server on cloud virtual machines
Manage your SQL Server instances running on cloud virtual machines — such as Amazon EC2 and Azure virtual machines. - Monitor hybrid environments with a single tool
Save time by using the same administration tool for SQL Server databases on-premises (on your physical and virtual machines); and in the private, public, and government cloud (on virtual machines). - Access mapped cloud drives
Get the most out of the cloud with cloud storage that is mapped as network drives or removable drives on Windows with SQL Admin Toolset. For example, map storage to Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and Azure Blob Storage.
- Install on cloud virtual machines
